PRBA Opposes NTSB’s Lithium Battery Recommendations Cites Risk to Medical Patients
PRBA Opposes NTSB’s lithium battery recommendations. The group warns that new rules could limit access to battery-powered medical devices. Many people depend on these devices for health and safety:
- At least 2.5 million individuals in the United States use durable medical equipment, which often relies on batteries.
- Restrictions may also affect military operations and industry growth.
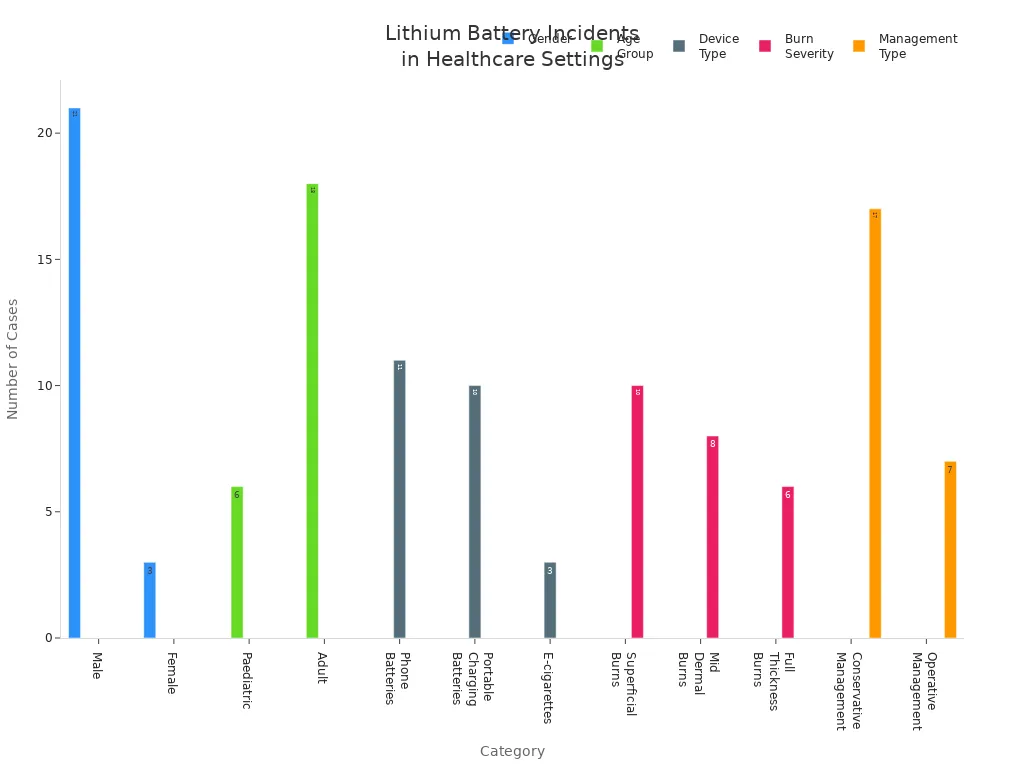
Recent healthcare data shows lithium battery incidents span all ages and device types.
Key Takeaways
- PRBA warns that NTSB's lithium battery recommendations could limit access to essential medical devices, impacting millions of patients who rely on them.
- Stricter regulations may delay the delivery of critical medical equipment, putting patients at risk, especially those with urgent health needs.
- The military's operational readiness could be compromised due to potential delays and increased costs in battery supply caused by new regulations.
- PRBA suggests alternatives to enhance lithium battery safety without hindering access, such as developing non-flammable batteries and promoting safe manufacturing practices.
- Balancing safety and access is crucial; effective solutions can protect patients while ensuring the availability of life-saving devices.
NTSB Recommendations

Overview
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) has released a set of recommendations to address the growing safety concerns related to lithium batteries. These recommendations focus on improving emergency response and reducing risks associated with battery-powered vehicles and devices. The NTSB aims to protect both the public and first responders from hazards such as fires and explosions that can occur during accidents involving lithium batteries.
The recommendations target several areas. They call for better emergency response guides from vehicle manufacturers. These guides should follow international standards and provide clear instructions for handling battery incidents. The NTSB also encourages ongoing research to find ways to safely manage energy left in damaged batteries, known as stranded energy. This research seeks to prevent further harm after an accident.
The NTSB’s approach highlights the need for clear, accessible information for those who respond first to emergencies involving lithium batteries.
Safety Goals
The main goal of the NTSB’s recommendations is to enhance safety for everyone who may encounter lithium battery incidents. The board wants to reduce the risk of thermal runaway, a dangerous chain reaction that can cause fires in high-speed crashes. The NTSB also stresses the importance of including vehicle-specific information in emergency guides, so responders know how to handle different types of battery fires.
The table below summarizes the key components of the NTSB’s recommendations and their intended safety improvements:
| Key Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Response Guides | Improve guides based on ISO 17840 and SAE J2990 standards. |
| Research on Stranded Energy | Continue research to mitigate or deenergize stranded energy in high-voltage batteries. |
| Thermal Runaway Hazards | Ongoing research to reduce hazards from thermal runaway in severe crashes. |
| Vehicle-Specific Information | Add specific instructions for handling battery fires and reducing risks. |
| First Responder Guidance | Provide information about fire risks and safe storage of damaged electric vehicles. |
These steps show the NTSB’s commitment to public safety. However, PRBA Opposes NTSB recommendations, raising concerns about the impact on access to essential medical devices and other critical services.
PRBA Opposes NTSB

Main Arguments
PRBA Opposes NTSB recommendations because the group believes the new rules could harm patients, disrupt military operations, and weaken the lithium battery industry. PRBA argues that the NTSB’s approach does not fully consider the real-world consequences for people who depend on battery-powered devices. The group also points out that the recommendations could create unnecessary regulatory burdens, making it harder for manufacturers to deliver safe and reliable products.
PRBA Opposes NTSB by stating that the proposed changes would not only increase costs but also slow down innovation. The organization stresses that many devices, especially those used in healthcare and defense, require specialized batteries that may not fit standard testing or packaging rules. PRBA believes that a one-size-fits-all approach could limit access to life-saving technology.
Medical Patient Risks
Many patients rely on battery-powered medical devices for daily living and emergency care. PRBA Opposes NTSB recommendations because stricter rules could delay or block the delivery of these essential devices. For example, new regulations might require extra testing or paperwork for batteries used in ventilators, infusion pumps, or portable oxygen concentrators. These delays could put patients at risk, especially those with chronic illnesses or urgent medical needs.
Common lithium battery failures in medical devices include:
- Capacity loss, which shortens device usage time.
- Swelling, which can damage the device or make it unsafe.
- Overheating, which may cause burns or fires.
- Short circuits, which can lead to sudden device failure.
- Voltage drops, which reduce performance.
- Charging issues, which prevent devices from working when needed.
PRBA Opposes NTSB because the group believes that new rules could make it harder for manufacturers to address these issues quickly. The organization warns that supply chain disruptions could lead to shortages or higher costs for patients.
Military and Industry Impact
The military depends on advanced lithium batteries for communication, navigation, and mission-critical equipment. PRBA Opposes NTSB recommendations because the group fears that new regulations could slow down the supply of batteries needed for defense operations. Delays in battery shipments or increased costs could affect military readiness and national security.
The lithium battery industry also faces challenges from stricter rules. Manufacturers must meet new requirements for testing, labeling, and packaging. These changes can increase production costs and slow down the introduction of new technologies. For example, compliance costs could reach $9.3 million in the first year and $70.2 million over ten years, according to government estimates. Industry groups warn that the total impact on the U.S. economy could reach $8.5 billion over a decade. Large companies like UPS project hundreds of millions of dollars in added expenses.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| New EU Liability Regulations | Increased demands for product failure investigations may become necessary to determine whether lithium-ion battery failures are due to a product issue or a repair action. |
| Impact on Economic Operators | The new EU Product Liability Directive places greater requirements on manufacturers, importers, distributors, and service providers to address potential liability considerations. |
| Circular Economy Considerations | The push towards circular economies generates additional safety, reliability, and liability considerations for products containing batteries. |
Stringent regulatory frameworks from agencies like the FDA also add to the cost and time needed to bring new medical devices to market. These factors can disrupt the supply chain and make it harder for patients and military personnel to get the equipment they need.
Evidence
PRBA Opposes NTSB claims about safety gaps in current lithium battery regulations. The NTSB has stated that some batteries, such as prototypes or those produced in low volumes, do not always undergo essential safety tests. These exemptions can increase the risk of battery fires, especially during air transport. PRBA argues that most manufacturers already follow strict safety standards and that additional rules may not provide significant benefits.
The group also highlights the most common types of lithium battery failures in medical and military devices. These include capacity loss, swelling, overheating, short circuits, voltage drops, and charging issues. PRBA believes that new regulations could make it harder to address these problems quickly, leading to more risks for users.
PRBA Opposes NTSB by pointing to the high costs of compliance. Estimates show that manufacturers could face millions of dollars in new expenses each year. These costs could slow down innovation, reduce competitiveness, and limit access to essential devices for patients and the military.
Perspectives
NTSB’s Rationale
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) places a strong focus on lithium battery safety because of several high-profile incidents and ongoing risks. The NTSB has investigated crashes involving lithium-ion batteries, such as the UPS cargo plane crash and the Asiana Airlines cargo jet crash. These events highlight the dangers that lithium batteries can pose during transport. The NTSB also found design and certification problems that could lead to serious accidents.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Incident Reports | Several crashes attributed to lithium-ion batteries, including a UPS cargo plane crash and an Asiana Airlines cargo jet crash. |
| Design Deficiencies | NTSB identified deficiencies in design and certification processes that could lead to catastrophic outcomes. |
| Regulatory Recommendations | NTSB recommends improving guidance and training for safety assessments related to new technologies. |
The NTSB stresses the urgent need for new regulations. Lithium batteries can cause fires and smoke, which threaten aircraft safety. The board points out that these risks require immediate action. The NTSB also wants to align U.S. rules with international standards and meet the requirements of the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2018. The board believes that better guidance and training will help prevent future accidents and protect both the public and first responders.
The NTSB’s recommendations aim to close safety gaps and reduce the risk of catastrophic events linked to lithium batteries.
PRBA’s Concerns
The PRBA and patient advocacy groups worry that new lithium battery regulations could limit access to essential medical devices. Many patients depend on devices powered by lithium batteries for daily care. New rules may make it harder to deliver these devices, especially in rural areas.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Prohibition of standalone lithium batteries | Standalone lithium batteries cannot be transported as cargo on passenger aircraft, affecting delivery to rural areas. |
| Shipping regulations | Batteries must be shipped at a state of charge not exceeding 30%, complicating immediate use for medical devices. |
| Need for government approvals | Transporting batteries at higher charges requires government approval, delaying access to essential medical devices. |
Patient groups highlight that shipping restrictions can delay or block the delivery of life-saving equipment. For example, if a battery arrives with a low charge, a patient may not be able to use a device right away. Waiting for government approval to ship batteries at a higher charge can add more delays. These challenges can have a direct impact on patient health and safety.
Patient advocates urge regulators to consider the real-world effects of new rules on people who rely on battery-powered medical devices.
Solutions
Alternatives
PRBA suggests several alternatives to improve lithium battery safety without limiting access to essential medical devices. The group recommends that manufacturers develop batteries that do not use flammable solvents. This change could reduce the risk of fires and explosions. PRBA also supports safer manufacturing processes for lithium batteries. These processes help prevent defects that might lead to dangerous incidents.
PRBA encourages regulations that focus on the safe use and storage of lithium battery products. Clear guidelines can help users handle batteries properly and avoid accidents. The group also believes in tracking and reporting injuries related to lithium batteries in a national database. This data can help experts understand how and why injuries happen. It can also guide future prevention efforts.
- Manufacturing lithium batteries without flammable solvents
- Promoting safe manufacturing processes
- Supporting regulations for safe use and storage
- Reporting and tracking injuries in a national database
These alternatives aim to address safety concerns while keeping essential devices available for patients and other users.
Balancing Safety
Balancing safety with access to battery-powered devices remains a key challenge. Accurate current measurement plays an important role in battery management. It helps estimate the state of charge and monitor performance. This information ensures that devices work reliably when needed.
Manual maintenance switches, or MSDs, provide a quick way to disconnect high-voltage circuits. These switches protect users and technicians during maintenance or emergencies. Certifications like CE and ETL confirm that products meet safety standards. These certifications also help devices reach markets in different regions.
Fire protection systems with VOC detection offer early warnings of battery problems. Early detection allows for fast action, reducing the risk of harm. These measures show that safety and access can go hand in hand. By using smart technology and strong standards, manufacturers can protect users without blocking access to life-saving equipment.
Patient safety and device availability both matter. Solutions that combine technology, clear rules, and careful monitoring can achieve both goals.
Experts in medical and military fields stress the need for strict safety standards and adaptable testing equipment. They also highlight new transport rules, such as labeling fire risks and shipping batteries at lower charges. Communities benefit when leaders understand local needs and protect access to essential services.
Any action involving critical infrastructure must not increase vulnerability or cause harm, directly or indirectly.
Balanced solutions help protect patients, support military operations, and encourage innovation without blocking vital devices.
-

 May.2025.12.22What is a Nickel Cadmium Battery and How Does It WorkLearn More
May.2025.12.22What is a Nickel Cadmium Battery and How Does It WorkLearn More -
 May.2025.12.22How to clean battery corrosion?Learn More
May.2025.12.22How to clean battery corrosion?Learn More -

 May.2025.12.2021700 Battery: Meaning, Comparison with 18650, and How to Choose the Best QualityLearn More
May.2025.12.2021700 Battery: Meaning, Comparison with 18650, and How to Choose the Best QualityLearn More -

 May.2025.12.19Medical Device 18650 Rechargeable Battery: What Buyers Must Evaluate?Learn More
May.2025.12.19Medical Device 18650 Rechargeable Battery: What Buyers Must Evaluate?Learn More -

 May.2025.12.19Common voltage types of lithium polymer batteries for different applicationsLearn More
May.2025.12.19Common voltage types of lithium polymer batteries for different applicationsLearn More