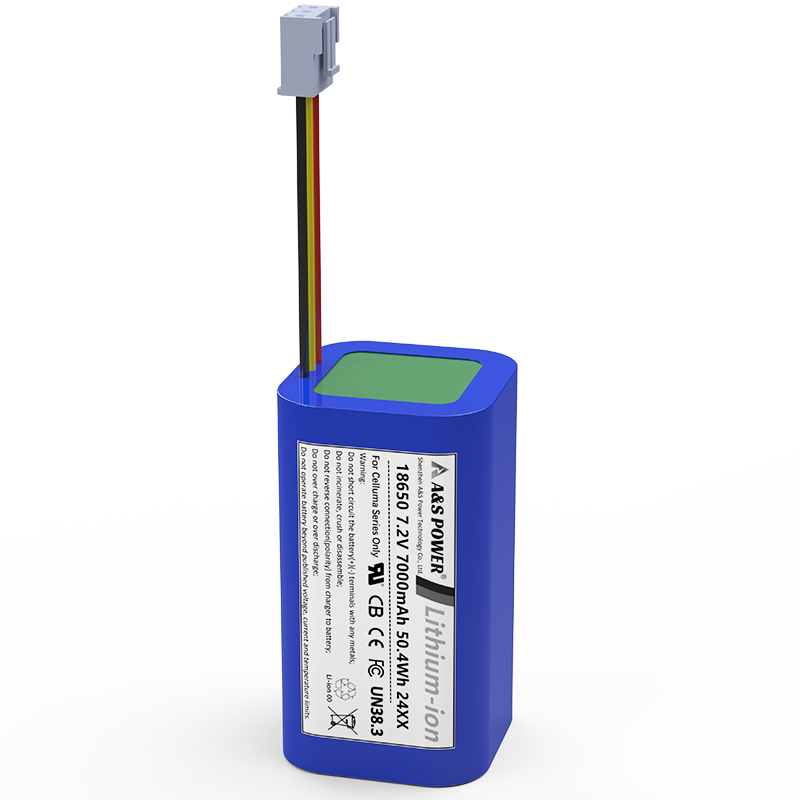
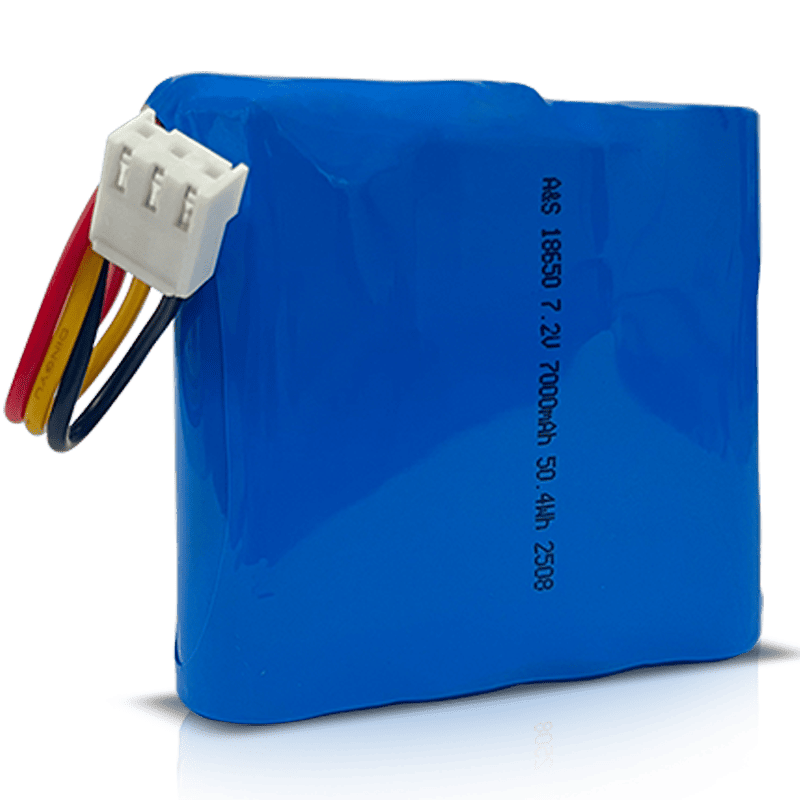
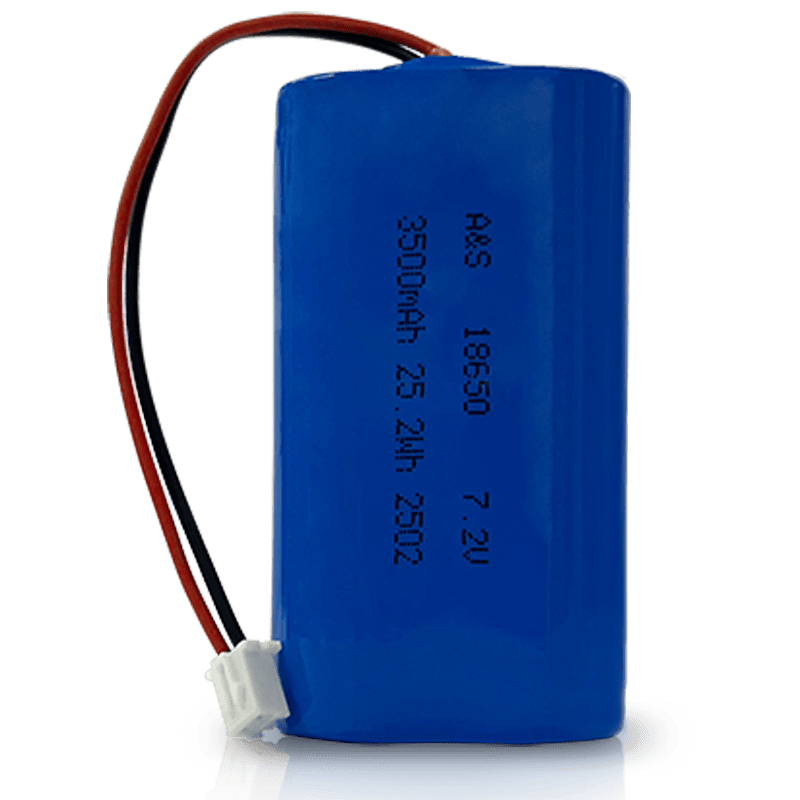
7.2V Li-ion Battery Pack – A Complete Technical & Application Guide
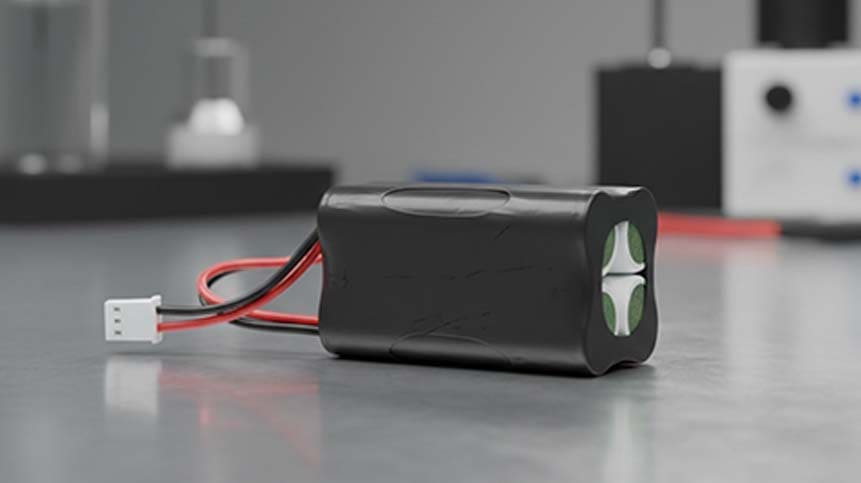

When customers ask us for a 7.2V Li-ion battery pack, they are usually not just looking for a voltage rating. They are looking for a stable, rechargeable, long-life power source that fits their device, meets safety regulations, and can be reliably manufactured at scale.
In this guide, I’ll break down how 7.2V lithium-ion battery packs are designed, where they are used, what specifications really matter, and how OEM customization works in real production scenarios—not theory.
What Is a 7.2V Li-ion Battery Pack?
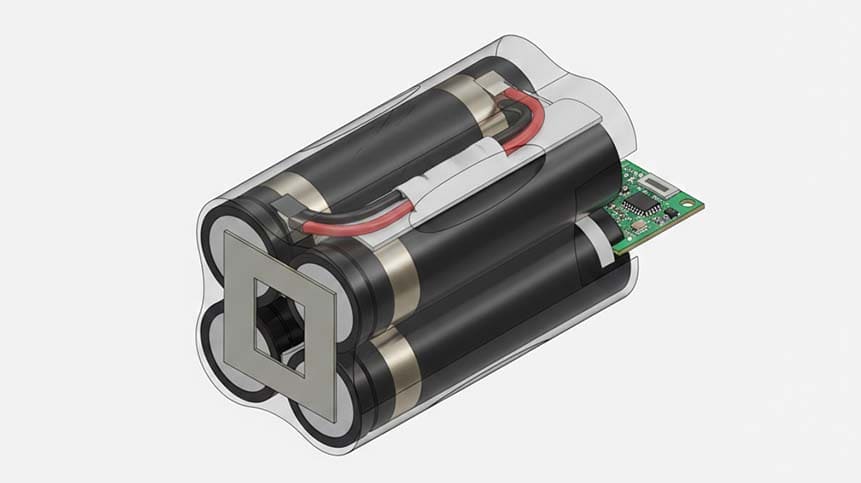
A 7.2V Li-ion battery pack is typically built by connecting two lithium-ion cells in series (2S configuration). Since a single Li-ion cell has:
-
Nominal voltage: 3.6–3.7V
-
Fully charged voltage: 4.2V
A 2S pack delivers:
-
Nominal voltage: ~7.2–7.4V
-
Fully charged voltage: 8.4V
This voltage level is extremely popular because it balances power capability, compact size, and electronic compatibility.
Common Cell Configurations for 7.2V Battery Packs
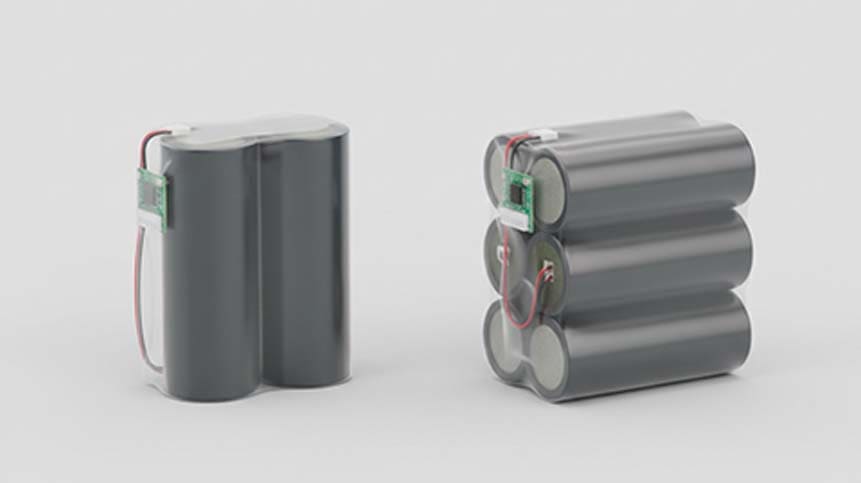

2S1P, 2S2P, and Beyond
|
Configuration |
Nominal Voltage | Typical Capacity Range | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2S1P |
7.2V | 1500–3500 mAh | Compact electronics |
|
2S2P |
7.2V | 3000–7000 mAh | Longer runtime devices |
|
2S3P+ |
7.2V | 7000 mAh+ | High-capacity equipment |
From our production experience, 2S1P and 2S2P are by far the most requested formats, especially in portable industrial tools, medical devices, and handheld electronics.
Key Electrical Specifications That Matter
When evaluating or sourcing a 7.2V Li-ion battery pack, these are the parameters engineers and buyers should focus on:
Voltage Profile
-
Nominal: 7.2V / 7.4V
-
Charge cut-off: 8.4V
-
Discharge cut-off: typically 5.0–6.0V (depends on BMS design)
Capacity (mAh / Wh)
Capacity directly affects runtime. In OEM projects, we always calculate Wh (Watt-hours) instead of mAh to compare energy fairly.
Example:
-
7.2V × 2600 mAh ≈ 18.7 Wh
Discharge Rate and Load Matching
Not all 7.2V Li-ion battery packs are designed for the same current output.
|
Discharge Type |
Typical C-Rate | Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Standard |
0.5C–1C | Sensors, controllers |
|
Medium |
2C–3C | Medical handhelds |
|
High-drain |
5C+ | Power tools, robotics |
Selecting the wrong discharge profile is one of the most common reasons for premature battery failure we see in customer prototypes.
Battery Management System (BMS) for 7.2V Packs
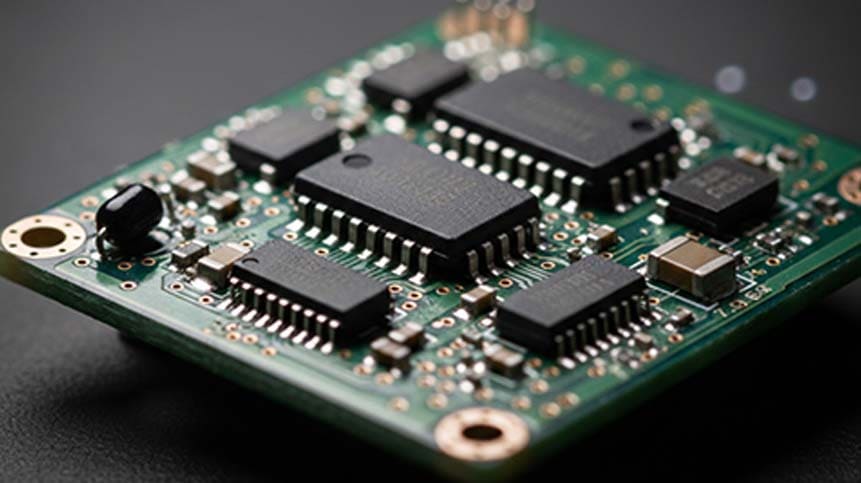

A BMS is not optional—it is mandatory for safety, compliance, and lifespan.
Core BMS Functions
-
Overcharge protection
-
Over-discharge protection
-
Overcurrent protection
-
Short-circuit protection
-
Cell balancing (recommended)
In higher-end designs, we also integrate:
-
NTC temperature monitoring
-
SMBus / I²C communication
-
Fuel gauge ICs
Safety Standards and Certifications
For global markets, a 7.2V Li-ion battery pack typically needs:
-
UL 2054 / UL 1642 – North American markets
-
CE / RoHS / REACH – EU compliance
Typical Applications of 7.2V Li-ion Battery Packs
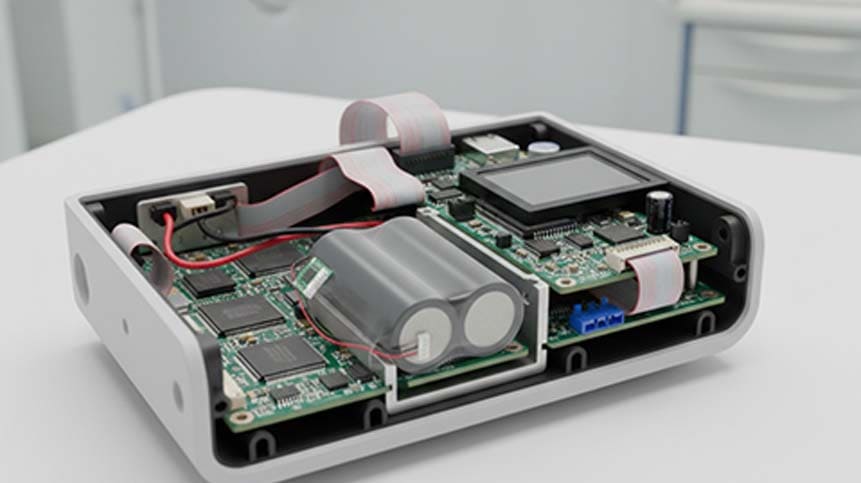

From real customer projects, the most common applications include:
-
Medical diagnostic equipment
-
Portable monitoring devices
-
Barcode scanners
-
Industrial handheld terminals
-
Test & measurement instruments
-
Consumer electronics requiring higher stability than 3.7V
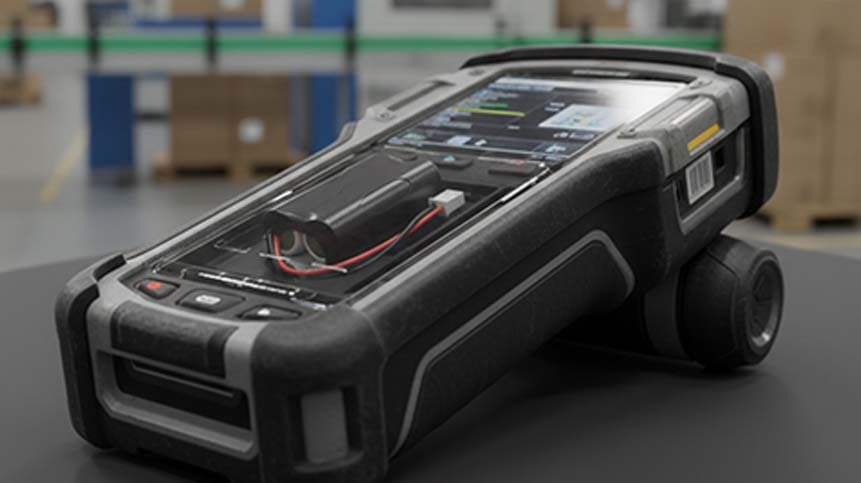

Why 7.2V Is Often Chosen Over 3.7V or 12V
|
Voltage |
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
3.7V |
Simple, cheap | Limited power |
|
7.2V |
Balanced power & size | Requires 2 cells |
|
12V |
High power | Larger, heavier |
In many designs, 7.2V becomes the “sweet spot”—enough voltage headroom without the inefficiency of step-up converters.
OEM & Customization Options
From an OEM perspective, customization usually includes:
-
Cell type (18650, 21700, Li-polymer)
-
Capacity matching
-
BMS logic customization
-
Connector type (JST, Molex, custom)
-
Cable length and gauge
-
Housing (PVC, shrink wrap, hard case)
-
Labeling & branding
This is where battery pack manufacturers create real value, not just selling cells.
Battery Lifespan and Cycle Performance
A properly designed 7.2V Li-ion battery pack typically delivers:
-
500–800 cycles at 80% capacity retention
-
More than 3–5 years of calendar life
Factors affecting lifespan:
-
Depth of discharge
-
Operating temperature
-
Charge current
-
BMS balancing quality
Typical 7.2V Li-ion Pack Performance
|
Parameter |
Typical Value |
|---|---|
|
Nominal Voltage |
7.2–7.4V |
|
Max Charge Voltage |
8.4V |
|
Capacity Range |
1500–10000 mAh |
|
Cycle Life |
500–800 cycles |
|
Operating Temp |
-20°C to +60°C |
FAQ – 7.2V Li-ion Battery Pack
Is a 7.4V battery the same as 7.2V?
Yes. The difference is naming convention. Both refer to 2-cell Li-ion packs.
Can I replace NiMH 7.2V with Li-ion?
Yes, but charging circuit and protection must be redesigned.
Do I need a custom charger?
Absolutely. A Li-ion charger must follow CC/CV charging at 8.4V.
What is the MOQ for custom packs?
Most OEM manufacturers start from 100–500 units, depending on design complexity.
References
-
 May.2026.02.097.2V Li-ion Battery Pack – A Complete Technical & Application GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.097.2V Li-ion Battery Pack – A Complete Technical & Application GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.06Lithium-Ion Battery Energy Density: How Much Energy Can We Really Store?Learn More
May.2026.02.06Lithium-Ion Battery Energy Density: How Much Energy Can We Really Store?Learn More -

 May.2026.02.05Smart Insulin Recorder Battery: Powering Accurate Diabetes Management DevicesLearn More
May.2026.02.05Smart Insulin Recorder Battery: Powering Accurate Diabetes Management DevicesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.04Small 12 Volt Rechargeable Battery: A Complete Professional GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.04Small 12 Volt Rechargeable Battery: A Complete Professional GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.02How Long Do Rechargeable Batteries Last?Learn More
May.2026.02.02How Long Do Rechargeable Batteries Last?Learn More




















