The protection measure and working theory of Lithium ion battery
You use lithium ion battery technology every day. It powers your phone, laptop, and other devices. Lithium-ion batteries make up about 70% of all rechargeable batteries in the world.
| Category | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Global Rechargeable Market | 70% |
| Consumer Electronics | N/A |
Safety is important for you and others. Some recent events show batteries can start fires or even explode. For example, a phone once made a plane turn back. A power bank caused a fire on an Air Busan flight. The most common problems are overheating, sparking, smoking, fires, and explosions.
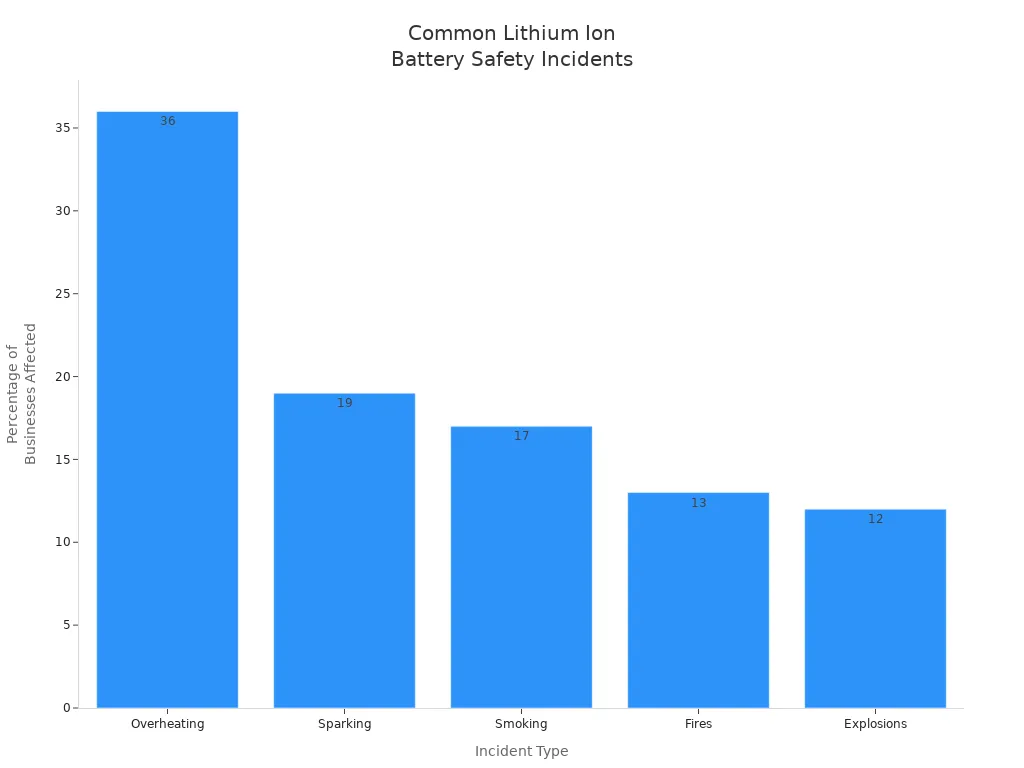
You need protection circuits and battery management systems. These help keep devices safe and make them last longer.
Key Takeaways
- Lithium-ion batteries are used in many devices. They make up 70% of rechargeable batteries. It is important to know their safety features for daily use.
- Protection circuits and battery management systems are very important. They stop overcharging and overheating. These problems can cause batteries to fail or catch fire.
- Charging lithium-ion batteries the right way is important. Use the constant current/constant voltage method. This keeps batteries safe and helps them last longer.
- Phosphate-based cathodes make batteries more stable in heat. They help stop overheating. This lowers the chance of fires in lithium-ion batteries.
- Always look for safety features in your devices. Check for protection circuits and battery management systems. This helps keep lithium-ion batteries safe and dependable.
How Lithium Ion Batteries Work

Structure and Components
You see lithium ion batteries in many devices. These batteries have different parts that work together. Each part uses special materials to help the battery work better and stay safe.
| Component | Material Types |
|---|---|
| Cathode | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2), Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC811), Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxide (LNMO) |
| Anode | Graphite |
| Electrolyte | Mixture of electrolyte salts in organic or inorganic solvents, available in aqueous or solid solutions |
- Cathode: You find materials like lithium iron phosphate and NMC in the cathode. These help the battery store energy and keep it safe.
- Anode: Most batteries use graphite for the anode. Some new batteries use silicon to hold more energy.
- Electrolyte: This liquid or gel lets lithium ions move between the cathode and anode.
- Separator: This thin layer keeps the cathode and anode apart. It stops short circuits and helps keep the battery safe. Some separators use ceramic coatings to handle more heat and stress.
Tip: The separator is very important for safety. It keeps the electrodes from touching and causing problems.
Intercalation and Deintercalation
You may wonder how lithium ion batteries store and give out energy. It happens when lithium ions move between the anode and cathode.
- When you charge the battery, lithium ions leave the cathode. They travel through the electrolyte to the anode. The anode has tiny spaces for the ions. More ions mean more stored energy.
- When you use the battery, the ions go back to the cathode. This gives power to your device.
- The number of ions moving decides how much energy the battery can hold and give.
- This movement also affects how long the battery lasts. Charging and using the battery many times can hurt the electrodes. Over time, this can crack or damage them and make the battery last less.
Note: The way the electrodes are made controls how many lithium ions can fit and how fast they move. Good design helps batteries last longer.
Charging Methods
You need to charge lithium ion batteries the right way. This keeps them safe and working well. Most devices use the constant current/constant voltage (CC-CV) method.
| Charging Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Constant Current (CC) | The battery charges quickly with a steady current until it reaches a set voltage. |
| Constant Voltage (CV) | The charger keeps the voltage steady and lowers the current to avoid overcharging. |
- The CC phase fills the battery fast. When the battery gets to the right voltage, the CV phase starts. The charger keeps the voltage steady and slowly lowers the current.
- This method stops the battery from getting too much charge. Overcharging can make the battery fail or catch fire. Not charging enough means you do not get full power.
- You see this charging method in phones, laptops, and electric cars. It helps batteries last longer and stay safe.
Remember: Charging the battery the right way is very important. Even small mistakes can hurt the battery or make it not last as long.
The Role of Phosphate-Based Cathodes in Thermal Stability
You want your lithium-ion battery to be safe, even when it gets hot. Phosphate-based cathodes, like lithium iron phosphate, help with this.
- These cathodes stop the battery from overheating. They keep working even when the battery gets hot.
- Other cathode materials, like NMC, can break down if they get too hot. This can cause fires or explosions.
- Many electric cars and power tools use lithium iron phosphate batteries for extra safety.
Safety Tip: Phosphate-based cathodes help make batteries safer for you and your devices.
Protection in Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium ion batteries help power your devices every day. These batteries need strong protection to stay safe and work well. Protection circuits and battery management systems watch each battery closely. They stop problems before they start. You can find these systems in phones, laptops, and electric cars. Let’s see what parts of a lithium battery keep you safe.
Protection Circuit Module (PCM)
Almost every lithium ion battery has a Protection Circuit Module. The PCM is like a guard for your battery. It looks for danger and stops unsafe things from happening.
- Overcharge protection stops charging past 4.2V. This keeps the battery from getting too hot or exploding.
- Over-discharge protection turns off power if voltage drops below 2-3V per cell. This saves the battery’s chemistry and helps it last longer.
- Overcurrent protection and short-circuit protection block too much current. They help prevent sparks and fires.
- Over-temperature protection uses sensors to check the battery’s heat. If the battery gets too hot, the PCM shuts it down.
- Cell balancing makes sure each cell in multi-series lithium-ion batteries charges and discharges evenly. This helps the battery keep its high energy and performance.
The PCM checks voltage and current all the time. If the battery goes past safe limits, the PCM disconnects it. You get fast protection that reacts to any problem.
Tip: Test your PCM often. Make sure it disconnects when voltage or current goes above safe levels. This keeps your lithium ion batteries safe.
Battery Management System (BMS)
Multi-series lithium-ion batteries need a battery management system. The BMS is smarter than a PCM. It tracks every cell and keeps the whole battery pack safe.
- The BMS watches cell voltage, current, and temperature. It checks for problems and keeps the battery working well.
- Protection features in the BMS stop overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal runaway. You get extra safety for your devices.
- Cell balancing in the BMS makes sure all cells have the same charge. This boosts capacity and energy output.
- The BMS sends data to your device. You can see battery status and health.
The BMS helps you get the most from your lithium ion batteries. It keeps performance high and makes batteries last longer. You see BMS in electric cars, power tools, and big energy storage systems.
Note: Without a BMS, lithium ion batteries can overcharge or over-discharge. This can cause fires, explosions, or loss of capacity.
Overcharge and Over-Discharge Protection
Overcharge protection and over-discharge protection are very important for lithium ion batteries. You need these features to keep your battery safe and strong.
| Protection Type | Voltage Threshold |
|---|---|
| Overcharge Protection | 4.2V |
| Over-discharge Protection | 2-3V per cell |
If you overcharge a battery, you risk damage. Metallic lithium can form on the anode, lowering capacity and causing safety problems. If you over-discharge, you increase pressure inside the battery. This destroys the active materials and shortens the battery’s life.
- Overcharge protection disconnects charging when voltage hits 4.2V.
- Over-discharge protection cuts off power if voltage drops below 2-3V per cell.
- Both protections keep your battery’s capacity and energy steady.
Alert: Charging above 4.35V can drop battery capacity to 85% after only 50 cycles. Over-discharging can cause permanent damage and raise resistance.
Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
Protection circuits stop overcurrent and short-circuit events. These problems can cause fires or explosions in lithium ion batteries.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Overcurrent Detection | Watches voltage across a sense resistor |
| Charge Control FET | Stops charge current |
| Discharge Control FET | Stops discharge current |
| Sense Resistor | Prevents heat buildup |
| Overcurrent Detection Pin | Checks voltage for overcurrent events |
The protection circuit watches the current flow. If it sees too much current, it disconnects the battery. You get fast protection that keeps your devices safe.
Safety Tip: Overcurrent protection and short-circuit protection are important for single-cell and multi-series lithium-ion batteries. Always use batteries with these features.
Thermal Safety Management
Heat is a big danger for lithium ion batteries. You need over-temperature protection and good thermal management to avoid problems.
- Air cooling moves heat away from the battery.
- Liquid cooling uses special fluids to keep batteries cool, especially in electric cars.
- Heat dissipation uses materials that spread heat quickly.
Thermal runaway can happen if the battery gets too hot. Causes include internal short circuits, overcharging, and bad battery management. You can stop thermal runaway by using strong safety systems and good protection circuits.
Note: Over-temperature protection shuts down the battery if it gets too hot. This keeps you and your devices safe.
Real-World Consequences of Protection Failures
You may see news about lithium ion batteries catching fire or exploding. Most accidents happen when protection circuits fail or are missing.
- Overcharging can cause metallic lithium to build up, leading to fires.
- Over-discharging can destroy battery materials and cause short circuits.
- Short-circuit events can spark explosions.
- Poor thermal management can lead to thermal runaway and device damage.
You should choose batteries with strong protection features. This keeps your devices safe and helps them last longer.
Ask yourself: Does your device have the right protection circuit and battery management system? If you have questions, reach out and learn more about how lithium ion batteries work.
Real-World Applications and Safety Features
Lithium ion batteries are in many things you use. You see them in phones, laptops, electric cars, and big energy storage systems. Each device uses special safety features to keep batteries safe.
Consumer Electronics
Your phone and laptop need lithium ion batteries to work. These devices use different safety steps to protect your data and hardware.
| Security Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Configure Security Settings | Set up device settings for optimal protection. |
| Use Antivirus Software | Install and update antivirus programs on laptops. |
| Enable Device Locks | Use password locks to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Disable Guest Accounts | Turn off guest accounts for better security. |
| Avoid Cleartext Passwords | Do not store passwords in unencrypted files. |
| Anti-Theft Software | Use software to locate your device if stolen. |
Battery Management Systems watch temperature, voltage, and current. BMS helps stop thermal runaway, swelling, and leaks. Always use the right charger and handle batteries gently to avoid harm.
Tip: If your battery gets swollen or leaks, take it out. Call the maker for safe disposal.
Electric Vehicles
Electric cars use big lithium ion battery packs. These batteries need strong safety features for fast charging and high power.
| Protection Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Short Circuit Protection | Stops damage from excessive current flow. |
| Battery Disconnect Systems | Allows safe disconnection in emergencies. |
| Thermal Management | Keeps batteries at safe temperatures. |
| Crash Protection | Protects batteries during collisions. |
| Battery Management System (BMS) | Monitors and manages battery safety and performance. |
| NHTSA Compliance | Meets safety regulations for electric vehicles. |
Car makers use cooling systems to control battery heat. Some use liquid cooling or special coolants. Charging stations have emergency shut-off switches for extra safety. These features help batteries work well and stay safe.
Industrial Uses
Factories and energy storage systems use lithium ion batteries for backup power. These batteries need strong protection in tough places.
- Overcharge and overdischarge protection keep batteries safe and make them last longer.
- Temperature checks change charging speed or disconnect batteries if it gets too hot or cold.
- Short circuit protection stops dangerous current fast.
Industrial batteries use advanced BMS and many safety layers. Designers add devices to break current and vents to stop failures. These systems protect your machines and keep energy steady.
Note: Past accidents helped improve safety designs. Now, lithium ion batteries are safer for you and your devices.
You have learned how lithium ion batteries work and why safety is important. Protection systems like PCM and BMS help keep your battery safe. They stop overcharge, over-discharge, and overheating. These features help your battery last longer and work better. Modern safety tools, like temperature checks and cell balancing, make batteries more reliable. When you pick a lithium ion battery, look for good safety features. This will help protect your devices and make them work well.
-
 May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More
May.2026.02.27Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Six Constraints Blocking the Path to PerfectionLearn More -

 May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.25Li-Polymer Battery 5000mAh: Complete Technical & OEM GuideLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More
May.2026.02.24The Unparalleled Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries Over Traditional BatteriesLearn More -
 May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More
May.2026.02.243.6 Volt Battery: Complete Technical Guide for Engineers & BuyersLearn More -
 May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
May.2026.02.24What Is a 3.8V LiPo Battery? A Complete Engineering & OEM GuideLearn More
















